Psychological well being of UK firefighters
A complete of 10, 649 firefighters responded to the questionnaire, representing roughly 24% of the UK’s complete firefighter workforce (Wolffe et al.18). Participant demographics had been analysed in Wolffe et al. 18, and weren’t discovered to considerably differ from the English firefighter inhabitants38 with respect to intercourse (p > 0.05), however appeared to under-represent youthful age classes, retained firefighters, and people belonging to an ethnic minority (p < 0.05)18.
Round 19% (n = 2019) of firefighters self-reported at the least one psychological well being situation. Determine 1 shows the vary and frequency of psychological well being issues chosen by firefighters, which is then in comparison with the prevalence of these situations within the basic English inhabitants (the place doable3). Notice that firefighters had been in a position to choose a couple of psychological well being situation.
Self-reports of hysteria had been most prevalent amongst surveyed firefighters (roughly 12%), adopted by melancholy (round 10%) and post-traumatic stress dysfunction (PTSD) (round 5%), as offered in Fig. 1. The prevalence of self-reported anxiousness and melancholy amongst surveyed firefighters was additionally considerably increased than that of the English inhabitants (Fig. 1, distinction in proportions take a look at p < 0.05).
Lower than 2% of surveyed firefighters reported obsessive compulsive dysfunction (OCD) (1.6%), consideration deficit hyperactivity dysfunction (ADHD) (0.6%), consuming issues (0.4%), bipolar dysfunction (0.3%), autism spectrum dysfunction (ASD) (0.2%), or schizophrenia (0.04%). The vast majority of firefighters who chosen “different” (0.4%) listed “stress” related to their work (40% of firefighters answering “different”, or 0.2% of complete surveyed firefighters).
Out of the 19% of surveyed firefighters struggling any psychological well being situation (n = 2019), round 44% reported having a couple of situation (n = 878). The frequency with which psychological well being situations co-occurred is displayed in Fig. 2. Nervousness and melancholy co-occurred most steadily.
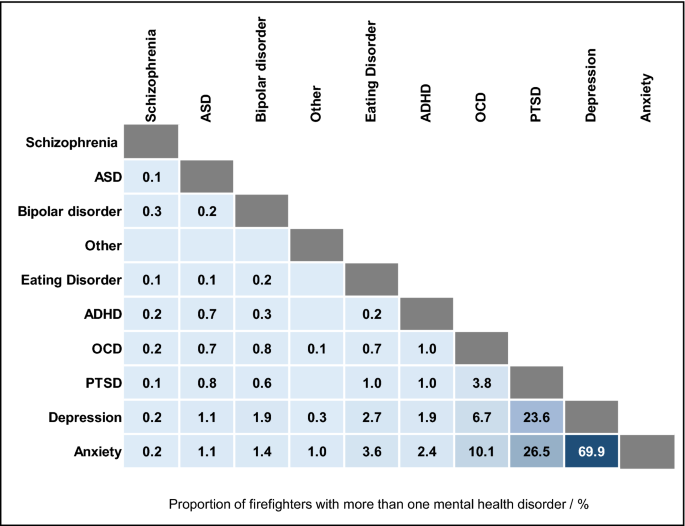
Firefighters’ Co-occurring Psychological Well being Circumstances. Proportion of firefighters with a couple of psychological well being situation (n = 878), who reported the co-occurrence of particular psychological well being situations. Clean cells point out that psychological well being situations didn’t co-occur amongst surveyed firefighters.
From the logistic regression fashions (Supplemental File S2), having a co-occurring psychological well being situation had essentially the most sizeable influence on reporting melancholy or anxiousness. Firefighters with at the least one co-occurring situation had been practically 16 occasions extra more likely to undergo melancholy (OR = 15.6, 13.3–18.4) and round 13 occasions extra more likely to undergo anxiousness (OR = 13.3, 11.5–15.5) when in comparison with firefighters with no co-occurring psychological well being situations (i.e. who solely had melancholy, or solely anxiousness).
Demographics
Related proportions of firefighters in every function, aside from essentially the most senior roles (equivalent to space or principal supervisor), had been discovered to undergo from any psychological well being situation, anxiousness, or melancholy, Fig. 3. The proportion of surveyed firefighters with any psychological well being situation, anxiousness, or melancholy typically elevated with size of service, Fig. 3. Firefighters who had served longer (i.e. ≥ 15 years) had been barely extra more likely to report struggling any psychological well being situation in comparison with firefighters who had served much less time (OR = 1.1, 1.0–1.3), though no vital variations had been noticed for anxiousness (OR = 1.0, 0.9–1.2) or melancholy (OR = 1.0, 0.9–1.2).
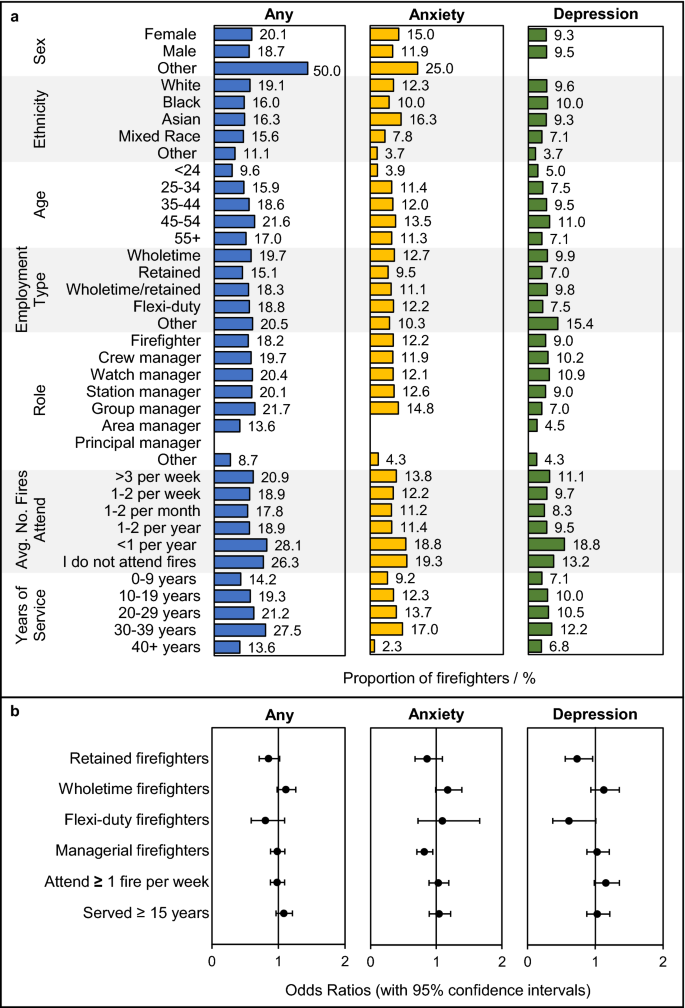
Firefighters’ Psychological Well being Circumstances by Demographics. (a) The proportion of firefighters with any psychological well being situation, anxiousness, or melancholy in every demographic class. (b) Odds ratios (with 95% confidence intervals) for particular demographic teams having any psychological well being situation, anxiousness, or melancholy. Notice that the proportions of surveyed firefighters in every demographic class are offered in Wolffe et al., 18. The outcomes of underpowered demographic teams (e.g. intercourse = “Different” for which there was a complete of 4 firefighters) ought to be interpreted cautiously. Odds ratios had been adjusted for numerous psychological well being danger elements (Supplementary File S2).
Solely wholetime firefighters, when in comparison with firefighters on all different contract varieties mixed, had been extra (however not considerably extra) more likely to report any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.1, 1.0–1.3), and anxiousness (OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.4).
Firefighters who attended fires on at the least a weekly foundation had been extra more likely to report melancholy in comparison with firefighters who attended fires much less steadily (OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.4). Nonetheless, no vital variations between these teams had been famous for any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.0, 0.9–1.1), or anxiousness (OR = 1.0, 0.9–1.2).
Well being and way of life
Firefighters had been additionally requested questions associated to their well being and way of life, which might presumably be linked with psychological well being situations equivalent to anxiousness, or melancholy (Supplemental File S1, Wolffe et al.18). These questions had been subsequently included in logistic regression fashions (Supplemental File S2) and are explored additional under.
Sleeping issues
Round 61% of all surveyed firefighters (n = 6490) stated that they’ve sleeping issues, Fig. 4a. Those that reported sleeping issues had been 4.2 occasions extra more likely to report any psychological well being situation (OR = 4.2, 3.7–4.9), 2.9 occasions extra more likely to report anxiousness (OR = 2.9, 2.4–3.5) and a couple of.3 occasions extra more likely to report melancholy (OR = 2.3, 1.9–2.8) in comparison with firefighters who didn’t report it, Fig. 4c.
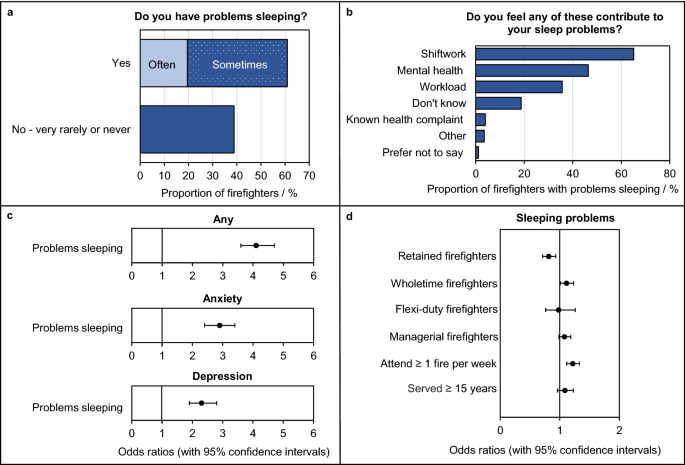
Firefighters’ Sleeping Issues. (a) The proportion of complete surveyed firefighters who indicated whether or not they had sleeping issues. (b) The proportion of firefighters with sleeping issues itemizing the explanations for his or her sleep disturbances. Notice that firefighters had been in a position to choose a couple of cause. (c) Adjusted odds ratios (with 95% confidence intervals) for firefighters’ psychological well being situations as a result of sleeping issues. (d) Adjusted odds ratios (with 95% confidence intervals) for firefighters sleeping issues as a result of demographic variables. Notice that odds ratios offered in (c) and (d) had been adjusted for quite a lot of disturbed sleep danger elements (Supplementary File S2).
Firefighters had been additionally requested to offer extra particulars about their sleeping issues. They had been in a position to choose a number of solutions, listed in Supplemental File S1. Over 65% of firefighters (out of 6490, n = 4228) indicated that shift work was a serious sleep disturbance (Fig. 4b). Psychological well being (46%, n = 3010) and workload (36%, n = 2313) had been additionally steadily chosen. Residence, private or family-life associated causes (e.g. disturbed by youngsters or break up/divorce and so on.) had been the most typical disturbances listed by firefighters choosing “different”.
A number of logistic regression analyses (Supplemental File S2) revealed a barely elevated probability of reporting sleeping issues for managerial firefighters (OR = 1.1, 1.0–1.2), wholetime firefighters (OR = 1.1, 1.0–1.2), firefighters attending fires on at the least a weekly foundation (OR = 1.2, 1.1–1.3), and firefighters with 15 + years of service (OR = 1.1, 0.9–1.2), Fig. 4d. Nonetheless, this improve was solely vital for firefighters attending incidents on a weekly foundation. Retained firefighters had been barely, however considerably, much less more likely to report sleeping issues when in comparison with firefighters employed on all different contract varieties mixed (OR = 0.9, 0.7–1.0).
Different well being and way of life variables
A number of different well being and way of life variables had been additionally discovered to be considerably related to firefighters’ psychological well being, and are offered in Desk 1.
Firefighters with a most cancers prognosis had been considerably extra more likely to report any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.5, 1.1–1.9), however weren’t discovered to be considerably extra more likely to report anxiousness (OR = 1.2, 0.9–1.7), melancholy (OR = 0.9, 0.6–1.3) or sleeping issues (OR = 1.0, 0.8–1.3).
Other than issues sleeping and having a co-occurring psychological well being situation, the one well being/way of life variables discovered to be considerably related with melancholy was rare exercising (OR = 1.4, 1.2–1.7). Extreme ingesting, smoking, and issues with blood stress had been discovered to be considerably related to each any psychological well being situation and sleeping issues (Desk 1).
Fertility issues had been considerably related to any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.4, 1.1–1.9), anxiousness (OR = 1.3, 1.0–1.7) and sleeping issues (OR = 1.3, 1.1–1.5).
Publicity to fireside contaminants throughout/after fireplace incidents
Considerably elevated odds ratios for any psychological well being situation had been discovered for firefighters who seen soot of their nostril/throat for greater than a day after attending a fireplace (OR = 1.8, 1.4–2.4), and for those who remained in PPE for greater than 4 h after a fireplace (OR = 1.9, 1.2–3.1). Outcomes are proven in Fig. 5. Firefighters had been additionally considerably extra more likely to report any psychological well being situation in the event that they reported nonetheless noticing the scent of fireside smoke on the physique after washing (OR = 1.3, 1.1–1.5), or consuming with sooty fingers (OR = 1.3, 1.1–1.4).
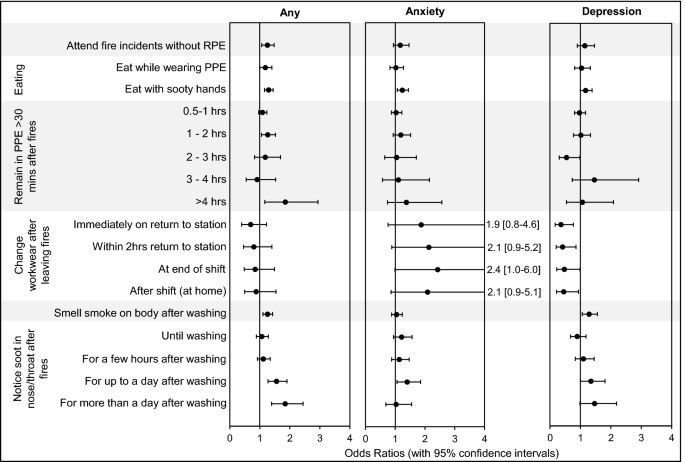
Firefighters’ Publicity to Contaminants Throughout/After Fires and Psychological Well being Odds Ratios. Odds ratios (with 95% Confidence Intervals) had been adjusted for numerous psychological well being danger elements (Supplementary File S2).
Related outcomes had been discovered for anxiousness. Considerably elevated odds ratios had been discovered for firefighters who eat with sooty fingers (OR = 1.2, 1.1–1.4 for anxiousness), and who seen soot within the nostril/throat for as much as a day after washing (OR = 1.4, 1.0–1.8 for anxiousness).
These noticing the scent of fireside smoke on the physique after washing had been considerably extra more likely to report melancholy (OR = 1.3, 1.0–1.5).
Hearth contaminants on firefighters’ PPE and at their office
Firefighters with ill-fitting PPE had been considerably extra more likely to report any psychological well being dysfunction (OR = 1.4, 1.2–1.7), and anxiousness (OR = 1.4, 1.1–1.7), offered in Fig. 6. Considerably elevated odds ratios had been additionally discovered for firefighters taking PPE residence (OR = 1.4, 1.2–1.6 for any psychological well being situation, OR = 1.3, 1.1–1.6 for anxiousness, and OR = 1.3, 1.0–1.6 for melancholy).
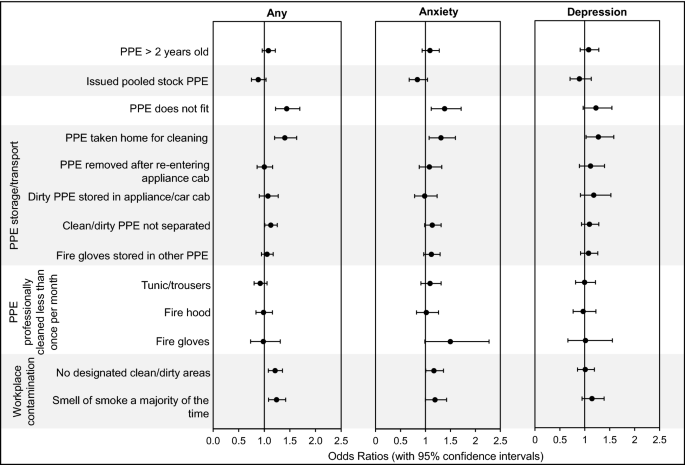
Firefighters’ PPE/Office Contamination and Psychological Well being Odds Ratios. Odds ratios (with 95% confidence intervals) had been adjusted for numerous psychological well being danger elements (Supplementary File S2).
Moreover, considerably elevated odds ratios had been discovered, for these firefighters failing to retailer clear and soiled PPE individually (OR = 1.1, 1.0–1.3 for any psychological well being situation (Fig. 6)).
Occasionally sending fireplace gloves for skilled decontamination was additionally related to an elevated anxiousness odds ratio (OR = 1.5, 1.0–2.3).
Firefighters who labored in stations with no designated clear and soiled areas had been additionally extra more likely to report any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.2, 1.1–0.4), and anxiousness (OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.4), as had been firefighters working in stations which scent of fireside (OR = 1.2, 1.1–1.4 for any psychological well being situation and OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.4 for anxiousness), Fig. 6.
Tradition, fireplace contaminant consciousness and coaching and tradition
Firefighters who personally imagine that contaminated PPE ought to be celebrated as a “badge of honour” (defined in Wolffe et al.18) had been considerably extra more likely to report any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.5, 1.2–1.7), or anxiousness (OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.5) (Fig. 7). Feeling that colleagues uphold this perception was additionally related to a barely elevated odds ratio for any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.3).
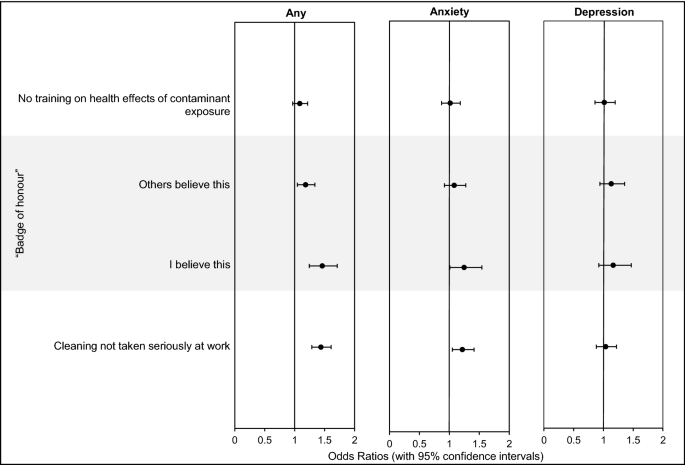
Firefighters Coaching/Tradition and Psychological Well being Odds Ratios. Odds ratios (with 95% confidence intervals) had been adjusted for numerous psychological well being danger elements (Supplementary File S2).
The opposite variables considerably related to any psychological well being dysfunction and anxiousness had been feeling that cleansing was not taken significantly on the office (OR = 1.4, 1.3–1.6 for any psychological well being situation, and OR = 1.2, 1.0–1.4 for anxiousness). As well as, firefighters who had not obtained coaching on the well being results of fireside contaminants had been solely barely (however not considerably) extra more likely to point out having any psychological well being situation (OR = 1.1, 1.0–1.2).
Source link
